AI algorithms are sets of instructions that help artificial intelligence systems process information, react to data, and make decisions on their own. Imagine these algorithms as the brain of a computer, helping it learn and adapt, much like how you learn from experience. Artificial intelligence uses these tools to handle new situations, not just follow the same rules every time. By understanding how AI works, you can see why AI systems power many artificial devices around you, from smart assistants to computer games.
Key Takeaways
- AI algorithms help machines learn from data, adapt, and make smart decisions without fixed rules.
- There are three main types of AI algorithms: supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning, each with unique ways to process data and solve problems.
- Deep learning uses neural networks with many layers to handle complex tasks like image and speech recognition automatically.
- AI algorithms power many everyday tools like smart assistants, recommendation systems, and self-driving cars, making life easier and more efficient.
- Choosing the right AI algorithm depends on your data, problem type, and resources, so understanding these factors leads to better AI solutions.
AI Algorithms
What Are AI Algorithms
You can think of AI algorithms as the step-by-step instructions that help artificial intelligence solve problems and make decisions. These artificial intelligence algorithms allow a computer to learn from data, spot patterns, and improve over time. Unlike traditional computer programs that follow fixed rules, AI algorithms can adapt and change based on new information. This makes artificial intelligence much more flexible and powerful in handling real-world tasks.
AI algorithms fall into several main categories:
- Supervised learning algorithms: You train these with labeled data, where each input has a correct answer. They help with tasks like sorting emails or predicting house prices.
- Unsupervised learning algorithms: These work with data that has no labels. They find hidden patterns or group similar items together, such as organizing photos by faces.
- Reinforcement learning algorithms: These learn by trial and error, receiving rewards or penalties for their actions. You see this in game-playing AI or robots learning to walk.
Some artificial intelligence algorithms combine these types, creating hybrid approaches for even better results.
Tip: AI algorithms can handle complex, unstructured data like images or text, while traditional computer programs work best with clear, simple rules.
| Feature | Traditional Algorithms | AI Algorithms (Machine Learning) |
|---|---|---|
| Approach | Follow fixed, rule-based logic | Learn from data and adapt |
| Learning | No learning capability | Improve with feedback |
| Flexibility | Manual updates needed | Adapt automatically |
| Error Handling | Fixed by programmers | Learn from mistakes |
| Data Dependency | Structured data | Unstructured data |
How AI Algorithms Work
You might wonder how AI works behind the scenes. Artificial intelligence algorithms follow a series of steps to turn raw data into smart decisions:
- Data Input: You start by collecting data, such as pictures, numbers, or text.
- Preprocessing: The algorithm cleans and organizes the data, fixing errors and filling gaps.
- Model Building: The AI creates a model to find patterns or make predictions.
- Training: The model learns from examples, adjusting itself to get better results.
- Testing and Validation: You check if the model works well with new data.
- Implementation and Feedback: The AI goes into real use, and you watch how it performs.
- Learning and Adaptation: Advanced artificial intelligence algorithms keep learning from new data, getting smarter over time.
AI algorithms give artificial intelligence the power to learn, adapt, and solve problems in ways that traditional computer programs cannot. This is why you see AI systems in so many parts of daily life, from voice assistants to self-driving cars.
Machine Learning Algorithms
Machine learning algorithms help you teach computers to learn from data and make decisions. These algorithms fall into three main types: supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning. Each type uses a different approach to process data and improve over time. You will see these methods in many AI systems, from voice assistants to recommendation engines.
Supervised Learning
Supervised learning is the most common type of machine learning. You use labeled data, which means each example in your dataset has both input features and a correct answer. The algorithm learns the relationship between the inputs and outputs during training. This process helps the model make accurate predictions or classifications on new data.
You can think of supervised learning like a student learning with an answer key. The student practices with questions and checks the answers to see what is right or wrong. Over time, the student gets better at solving similar problems.
Supervised learning algorithms handle two main tasks:
- Classification: The algorithm sorts data into categories. For example, it can decide if an email is spam or not spam. You use classification in fraud detection, medical diagnosis, and image recognition.
- Regression: The algorithm predicts continuous values. For example, it can estimate house prices or forecast sales. Regression is important in finance, real estate, and weather forecasting.
Here is a table showing some of the most common machine learning algorithms used in industry today:
| Algorithm Name | Type of Learning | Typical Industrial Use Cases and Description |
|---|---|---|
| Linear Regression | Supervised Learning | Predicts continuous values, e.g., estimating costs or sales based on input variables. |
| Logistic Regression | Supervised Learning | Binary classification, e.g., fraud detection, marketing response prediction. |
| Decision Trees | Supervised Learning | Classification with multiple classes, branching outcomes based on features. |
| Random Forests | Supervised Learning | Ensemble of decision trees to improve accuracy and robustness in predictions. |
| Naïve Bayes Classifier | Supervised Learning | Probabilistic classification based on Bayes’ theorem, efficient and accurate. |
| Support Vector Machine (SVM) | Supervised Learning | Used for both regression and classification by finding optimal boundaries between classes. |
You will find supervised learning in many industries. For example, healthcare uses it for early disease detection, and retail uses it for price optimization. Companies rely on these algorithms for predictive modelling and to improve business outcomes. Studies show that supervised learning models like Random Forests and Linear Regression often achieve high accuracy in commercial applications.
The process for supervised learning usually follows these steps:
- You collect labeled data with input features and correct outputs.
- The algorithm learns from this data, adjusting its internal settings to reduce errors.
- You test the model on new data to check its accuracy.
- The model makes predictions or classifications on future data.
Tip: Supervised learning works best when you have lots of labeled data and need high accuracy for tasks like classification or regression.
Unsupervised Learning
Unsupervised learning algorithms work with data that has no labels. You use these algorithms to find patterns, group similar items, or detect unusual data points. The computer explores the data and discovers hidden structures on its own.
Imagine you have a box of mixed buttons. You ask the computer to sort them, but you do not tell it what the groups should be. The algorithm looks for similarities and creates clusters based on size, color, or shape.
Some popular unsupervised learning algorithms include:
- K-Means Clustering: Groups data into clusters based on similarity.
- Isolation Forest: Detects anomalies or outliers in large datasets.
- Dimensionality Reduction Algorithms: Simplify complex data for easier analysis.
You will see unsupervised learning in many areas:
- Market segmentation: Grouping customers by buying habits.
- Anomaly detection: Spotting fraud in financial transactions.
- Medical imaging: Identifying patterns in scans.
- Social network analysis: Finding communities in online platforms.
- Natural language processing: Organizing documents by topics.
Unsupervised learning helps you explore data, prepare it for further analysis, and uncover insights you might miss otherwise. However, it comes with challenges. You do not have ground truth labels, so measuring accuracy is harder. The results can depend on the algorithm and how you set its parameters. Sometimes, the patterns found may not have clear real-world meaning.
Note: Unsupervised learning is powerful for discovering unknown patterns, but you need to interpret the results carefully and sometimes combine it with other methods for the best outcome.
Reinforcement Learning
Reinforcement learning is a special type of machine learning where an agent learns by interacting with its environment. The agent takes actions and receives feedback in the form of rewards or penalties. Over time, the agent learns to choose actions that maximize its total rewards.
Think of reinforcement learning like training a dog. You give treats for good behavior and gentle corrections for mistakes. The dog learns which actions lead to rewards and repeats them.
Reinforcement learning algorithms use several key components:
| Component/Step | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Agent | The decision-maker performing actions in the environment. |
| Environment | The system or world where the agent operates. |
| State | The current situation or condition of the agent. |
| Action | Possible moves or decisions the agent can make. |
| Reward | Feedback from the environment based on the agent’s action, positive or negative (penalties). |
| Policy | Strategy mapping states to actions, guiding the agent’s decisions. |
| Value Function | Estimates future cumulative rewards from a given state, helping evaluate long-term benefits. |
The learning process involves:
- The agent explores different actions to see what happens.
- After each action, the environment gives a reward or penalty.
- The agent updates its strategy to favor actions that bring higher rewards.
- Over many tries, the agent improves and learns the best way to act.
Reinforcement learning has made a big impact in several industries:
| Industry | Reinforcement Learning Application | Impact / Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Financial Services | Customer retention, revenue growth, personalized marketing | 73% of AI-using companies saw 45% increase in customer satisfaction; Amazon's RL increased sales by up to 10% |
| Healthcare | Predictive engagement, personalized treatment plans | Medication adherence programs improved adherence rates by up to 25%, leading to better patient outcomes |
| Retail & E-commerce | Personalized recommendations, dynamic pricing, chatbots | Amazon: 10% sales increase, 20% customer engagement increase, 15% reduction in churn; Netflix improved customer retention; Walmart uses dynamic pricing; Spotify uses RL for music recommendations |
| Customer Service | RL-powered chatbots and virtual assistants | Improved customer satisfaction and reduced support queries; Salesforce and HubSpot implementations reported 45% increase in satisfaction |
You will find reinforcement learning in robotics, game playing, self-driving cars, and personalized recommendations. The agent learns through trial and error, always aiming to improve its performance.
Tip: Reinforcement learning is ideal for situations where you want an AI to learn from experience and adapt to changing environments.
Deep Learning
Neural Networks
You can think of neural networks as the backbone of deep learning. These networks work by mimicking how your brain processes information. Each neural network has layers made up of tiny units called neurons. These neurons receive data, perform calculations, and pass the results to the next layer. The process starts with the input layer, moves through one or more hidden layers, and ends at the output layer.
Here is how the main parts of a neural network work together:
- Neurons receive signals and calculate weighted sums.
- Activation functions add non-linearity, helping the network learn complex patterns.
- Layers organize neurons into input, hidden, and output groups.
- Weights and biases control how signals move and change.
- Loss function measures how far the network's answer is from the correct one.
- Optimization algorithms adjust weights and biases to improve accuracy.
- Backpropagation helps the network learn by updating weights based on errors.
When you train a neural network, it learns by comparing its answers to the correct ones. It then changes its weights and biases to get better over time. This process allows deep learning algorithms to handle large amounts of data and find patterns that are hard for humans to spot.
Note: Deep learning stands out from other machine learning methods because it uses deep, multi-layered neural networks. These networks can automatically learn features from raw data, which means you do not need to tell the AI what to look for.
Real-World Examples
You see artificial intelligence algorithms making a real difference in many industries. Companies use these algorithms to boost efficiency, save money, and improve accuracy. Here is a table that shows how different organizations use artificial intelligence and the benefits they gain:
| Company | AI Application | Measurable Improvement | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Whirlpool | RPA in manufacturing | Enhanced accuracy and productivity | Automation of repetitive tasks, quality control |
| Ajinomoto | RPA in finance/accounting | Saves over 230 hours per month | Time savings, reduced manual errors |
| Infineon Technologies Austria | AI for energy efficiency | Optimized supply chain and resource use | Sustainability, cost savings |
| Gerdau | AI-driven process optimization | Reduced alloy costs by $3/ton, lower CO₂ emissions | Cost savings, environmental benefits |
You also find artificial intelligence algorithms in logistics, healthcare, finance, and retail. For example, logistics companies use ai to optimize routes and cut costs by 15%. Healthcare providers use ai for personalized treatment plans, reducing documentation time by 42%. Retailers see up to a 30% sales boost from personalized recommendations. These applications of artificial intelligence show how ai can solve real problems and deliver measurable results.
Everyday Uses
You interact with ai every day, often without noticing. Artificial intelligence algorithms power smart assistants like Amazon Alexa and Google Home. These devices use natural language processing to understand your voice and help you with tasks. In your home, ai runs robotic vacuums and smart washing machines, making chores easier.
Many companies use ai to personalize your experience. Streaming services suggest movies you might like. Online stores recommend products based on your shopping habits. Fashion and beauty brands use ai to match products to your skin tone or style. Even food and beverage companies create custom flavors using ai applications that analyze taste and aroma.
In the background, artificial intelligence algorithms help with quality control in manufacturing and optimize supply chains. Logistics companies use ai for anticipatory shipping, preparing orders before you even place them. Marketing teams use ai to automate ads and engage customers in new ways. These applications of artificial intelligence make your daily life smoother, more efficient, and more personal.
Tip: You benefit from ai every time you use a smart device, shop online, or get a recommendation tailored just for you. The applications of artificial intelligence continue to grow, making technology smarter and more helpful.
Choosing AI Algorithms
Factors to Consider
When you choose ai algorithms, you need to look at several important factors. Start by understanding your data. Plot and explore your data to see how features relate to your target. If you notice a linear relationship, you might begin with simple models. For example, linear regression works well when your data shows a straight-line pattern. If your data is more complex, you may need non-linear models.
Think about the type of problem you want to solve. Are you working on classification, regression, or clustering? The number of features and the size of your dataset also matter. Large datasets allow you to use more advanced ai models, while smaller datasets may require simpler approaches. You should also consider how much interpretability you need. Simple models like linear regression or small decision trees are easier to explain, but deep learning models can be harder to understand.
Computational resources play a big role. Training large ai models often needs powerful GPUs and lots of memory. If you have limited resources, you may need to use cloud services or choose smaller models. Always balance efficiency and cost with your goals.
Tip: Focus on the quality of your data and make sure you have enough examples for training and testing. Good data leads to better learning and higher efficiency.
Matching Algorithms to Problems
You can match ai algorithms to your problem by following a few steps:
- Identify your problem type: Is it classification, regression, or something else?
- Check your data: Is it structured, like tables, or unstructured, like images or text?
- Decide how much data you have: More data lets you use complex models.
- Think about efficiency: Choose models that fit your hardware and time limits.
- Consider interpretability: Pick models you can explain if needed.
Here is a quick guide:
| Problem Type | Data Type | Recommended Algorithm |
|---|---|---|
| Classification | Structured | Decision Trees, SVM |
| Regression | Structured | Linear Regression, XGBoost |
| Classification | Images | Deep Learning (CNN) |
| Regression | Time Series | LSTM, ARIMA |
You should also involve domain experts to guide your choices. They help make sure your ai solution fits real needs. Always monitor your models and update them as your data changes. This keeps your ai efficient and reliable.
Note: Automate repetitive tasks with ai to boost efficiency and free up time for more important work.
Future of AI and Machine Learning
Trends
You will see many exciting trends shaping the future of artificial intelligence. These trends make technology smarter and more useful in your daily life.
- Deep learning keeps improving. New models like convolutional neural networks help computers recognize images, while recurrent neural networks help with language tasks.
- Reinforcement learning lets machines learn from trial and error. This trend powers self-driving cars and smart robots.
- Natural language processing is getting better. You can now talk to chatbots and virtual assistants that understand you more easily.
- AI systems can adapt to new situations. They change how they work based on real-time data, making decisions faster and more accurately.
- Generative AI models are becoming easier to use. The focus is moving from just performance to trust and how well these models work with older systems.
- Many AI tools are now made for specific jobs or industries, not just general use.
- Agentic AI models can make decisions and complete tasks on their own. This brings new opportunities and also raises questions about safety and ethics.
- AI literacy is important for everyone. You need to know how to use and understand these tools, not just how they work inside.
- Ethical challenges are growing. Designers must balance benefits and risks to make sure AI helps society.
Impact
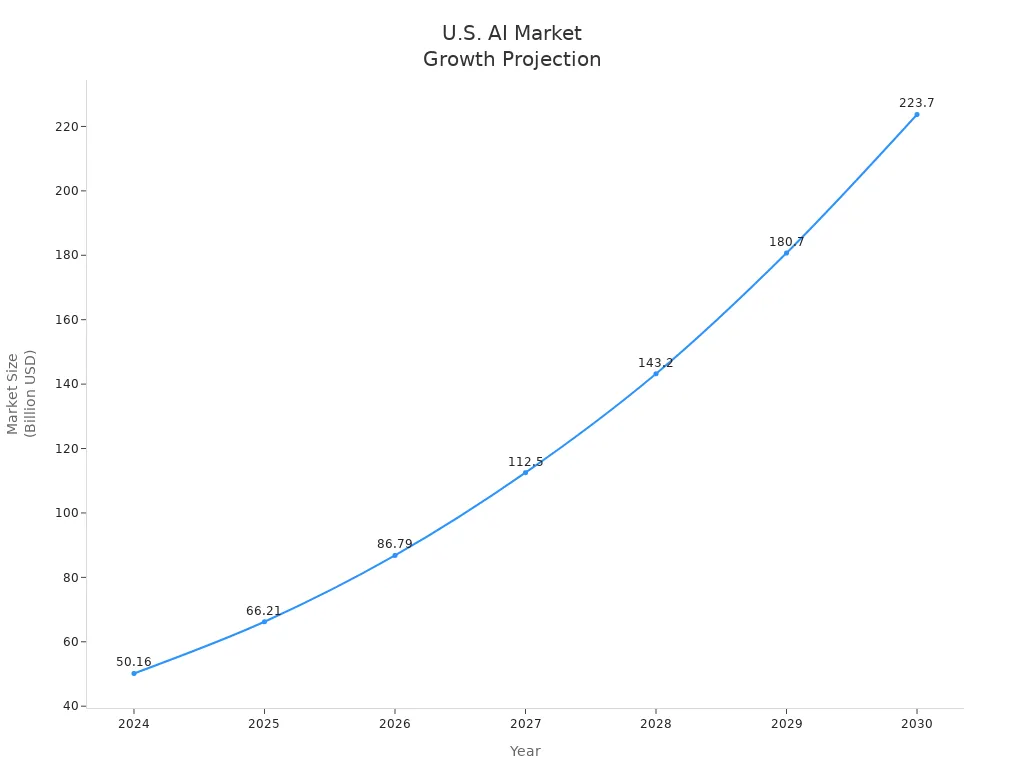
AI will change many industries and your everyday life. The market for artificial intelligence is growing fast. Look at the chart below to see how the U.S. AI market is expected to grow:
Here is how AI will impact some key industries:
| Industry | AI Applications | Expected Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | Improves diagnosis, automates image analysis, personalizes treatments | Earlier detection, better outcomes, fewer errors |
| Finance | Automates risk checks, detects fraud, manages investments | Real-time fraud prevention, smarter investments |
| Transportation | Powers self-driving cars, optimizes traffic, improves safety | Fewer accidents, smoother traffic, safer roads |
You may also notice changes in privacy and jobs. AI collects lots of data, which can affect your privacy. Some jobs may change or disappear, but new jobs will appear that need AI skills. Ethical questions about fairness, transparency, and decision-making will become more important. You will need to learn how to use AI responsibly and understand its effects on society.
You have learned that artificial intelligence algorithms help machines learn, solve problems, and make decisions. These tools include supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning, as well as deep learning for complex data. Understanding artificial intelligence prepares you for new opportunities and helps you use technology safely and wisely.
Experts believe artificial intelligence will drive major advances in science, healthcare, and education.To keep learning:
- Study basic algorithms and how they work.
- Practice with real-world projects.
- Stay updated on new trends and ethical guidelines.The future of artificial intelligence holds exciting possibilities for everyone.
FAQ
What are the main types of AI algorithms?
You will find three main types: supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning. These machine learning algorithms help computers learn from data, make predictions, and improve accuracy. Deep learning algorithms use neural networks for complex tasks like image recognition and natural language processing.
How do AI algorithms improve efficiency and accuracy?
AI algorithms process large amounts of data quickly. You can use them for classification, regression, and predictive modelling. They adapt to new information, which boosts efficiency and accuracy in many applications of artificial intelligence, such as healthcare, finance, and transportation.
Where do you see AI applications in daily life?
You interact with AI systems every day. Smart assistants, online recommendations, and self-driving cars all use artificial intelligence algorithms. These applications of artificial intelligence rely on machine learning, deep learning, and natural language processing to make your life easier and more efficient.
How do neural networks work in deep learning?
Neural networks use layers of artificial neurons to process data. You give the network input, and it learns patterns through training. Deep learning algorithms use these networks for tasks like speech recognition, image classification, and prediction in AI applications.
What should you consider when choosing an AI algorithm?
You should look at your data type, problem requirements, and available resources. Some algorithms work better for structured data, while others handle images or text. Always match the algorithm to your goal, whether it is classification, regression, or reinforcement learning.